Insomnia is an epidemic disorder that plagues millions of individuals around the world. It’s still widely misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed, and millions are struggling to cope with its effects. The purpose of this article is to clarify the causes, symptoms, and treatments of insomnia so that we can better sleep and live healthier lives.
Table of Contents
What is Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by struggling to fall asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and not being able to return to sleep. It’s not simply a rare sleepless night: insomnia is a major disruption to your normal life, in terms of physical, emotional and mental wellbeing. The condition might be short-lived (lasting just a few days or weeks), or chronic (lasting months or years).
Causes of Insomnia
Insomnia causes vary from individual to individual. The diagnosis of the condition requires a deep understanding of these causes. A few common causes of insomnia are listed below:
1. Stress and Anxiety
Stressful life experiences, whether they be professional pressures, financial issues or private relationships, can result in intense insomnia. Sleep issues are often exacerbated by anxiety disorders such as generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder.
2. Depression
Depression and insomnia can be correlated. While depression might create sleep issues, insomnia can exacerbate depressive symptoms, so it is a vicious cycle.
3. Poor Sleep Habits
Disordered sleep cycles, long periods before bed spent in front of a screen, and late-night consumption of stimulants such as caffeine all interfere with our body’s natural sleep-wake rhythm.
4. Medical Conditions
Sleep is disrupted by chronic pain, breathing difficulties, acid reflux and neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s. Sleep apnea, where breathing stops during sleep, is another major factor in insomnia.
5. Medications
Certain drugs, such as antidepressants, corticosteroids, and high blood pressure medications, can interrupt sleep.
6. Lifestyle Factors
Working shifts, travelling, and jet lag can wreak havoc on the circadian clock, which means it’s hard to maintain a healthy sleep cycle.
7. Substance Use
Alcohol, nicotine and recreational drugs affect sleep. Although alcohol can initially make you sleepy, in the long run, it disrupts sleep, resulting in a poor night’s sleep.
Symptoms of Insomnia
Sleeplessness comes in different forms, and symptoms range from mild to debilitating. Common symptoms include:
- Hard to Get Sleep: During the night you are lying awake for several hours before falling asleep.
- Frequent Nightwaking: Waking several times a night and struggling to fall asleep.
- Morning Awakening: Wake up earlier than you planned to and cannot fall back asleep.
- Chronic Daytime Fatigue: Getting tired or sleepy during the day even though you’ve had a decent amount of sleep in bed.
- Sleepiness and Mood Swings: Getting more irritable, anxious or depressed due to sleepiness.
- Cognitive Impairments: Impaired concentration, memory loss, lower performance.
Types of Insomnia
Knowing the forms of insomnia can provide insights into how to treat them:
1. Acute Insomnia
Such short-term insomnia is often caused by an event such as stress, illness or a life transition. Usually, it goes away after the cause has been solved.
2. Chronic Insomnia
Chronic insomnia occurs when the sleeping pattern persists for three nights a week or longer. It can be caused by chronic stress, disease or long-term insufficient sleep.
3. Onset Insomnia
This is the one that causes you to have trouble sleeping in the middle of the night. This is typically associated with anxiety or worrying too much.
4. Maintenance Insomnia
Maintenance insomnia is when you find it hard to sleep or wake up in the middle of the night. It is most often accompanied by a medical or psychological problem.
Solutions for Insomnia
Managing insomnia requires a multi-faceted strategy that fits the individual. Here are a few scientifically supported ways to get more good sleep:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
CBT-I is considered the gold standard for solving chronic insomnia. It involves:
- Sleep Limitation: Cut back on the amount of time spent in bed to help optimize sleep performance.
- Stimulus Control: Linking the bed to sleep by not watching TV or using a phone while in bed.
- Cognitive Reinvention: Resolving negative beliefs and thoughts about sleep.
- Relaxation Methods: Mindfulness, progressive muscle relaxation, or deep breathing.
2. Improving Sleep Hygiene
Getting good sleep habits in place can go a long way. Key practices include:
- Maintaining a Sleep Routine: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Making Atmosphere for Sleep: You need to keep the bedroom dark, quiet and cool.
- Be Aware of Screen Time: Stay away from electronic devices for at least one hour before going to bed.
- Skip Stimulants: Limit caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol consumption, especially late in the day.
3. Medications
In severe cases, doctors may prescribe benzodiazepines, non-benzodiazepine hypnotics or melatonin receptor agonists. However such medications need to be taken very carefully and under medical supervision as they could lead to dependence and side effects.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Sleep can be helped by adding some physical activities, including walking on a regular basis. However, you should be aware of vigorous exercise near bedtime. Creating a bedtime routine that involves reading or bathing in warm water can also remind the body to rest.
5. Alternative Therapies
Others experience relief with alternative treatments like acupuncture, yoga or aromatherapy. Relaxation may also be aided by herbal medications such as valerian root or chamomile tea, but these should only be tried with the guidance of a doctor.
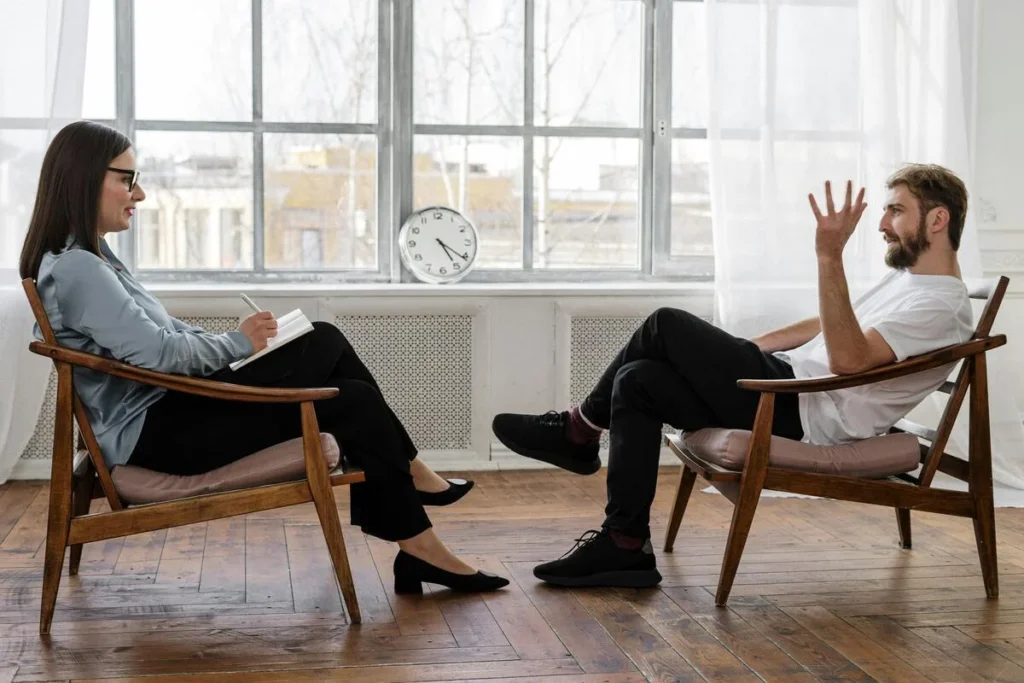
When to Seek Professional Help
Though insomnia is usually minor, chronic insomnia requires professional care. Talk to a physician or sleep specialist if:
- Sleep deprivation lasts longer than three months.
- Sleep deprivation affects daily activities and performance.
- The signs and symptoms of an underlying medical or psychological problem (chronic pain, depression, anxiety).
The Importance of Sleep
Sleep is not a luxury, it is essential to physical and mental health. Sleep repairs tissue, consolidates memories and balances hormones. Chronic insomnia has the potential to make people vulnerable to heart disease, diabetes, and compromised immune systems.
Final Words
Sleeplessness is an enigma that needs to be studied thoroughly to discover its causes, symptoms and treatments. As long as people make the necessary changes to their sleep routines, seek treatment and resolve underlying causes, they can enjoy sound sleep and enjoy a better quality of life. If you or a loved one are experiencing insomnia, know that support is out there and that sleeping well can be achieved.